- Documentation
- Video Call
- Upgrade using advanced features
- Advanced features
- Mix the video streams
Mix the video streams
Introduction
Through the stream-mixing service, multiple published media streams can compose a single stream , which allows audiences to play just one stream to improve quality and reduce performance cost.
ZEGOCLOUD supports using stream mixing with three methods, manual stream mix, automatic stream mix, and full-automatic stream mix. The following table shows their differences:
| Method | Manual |
Auto |
Full-Auto |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Customize the stream mixing tasks and content, including input stream, layout, etc. Supports mixing audio/video streams. |
In specified rooms, automatically mixing the audio streams. Only supports mixing the audio streams. |
In each room, automatically mix the audio streams. Only supports mixing the audio streams. |
| Scenario | Co-hosting across rooms, video/audio streams mixing, and specified stream mixing, etc. |
Audio-only scenarios. |
Audio-only scenarios. |
| Pros | Flexible and enable you to implement logic according to business needs. |
It reduces the complexity of integration, and does not required to manage the audio stream list of the specified rooms. |
With very low complexity of integration, and does not required to manage the in-room audio stream mixing task and audio stream list. |
| Relation with the server | The client side initiates the stream mixing task and manages the stream list. |
The client side initiates the stream mixing task, and the ZEGO server automatically manages the in-room input stream list. |
The ZEGO server manages the stream mixing tasks and the in-room stream list. |
Use cases
You can use stream mixing for various use cases. The following are some typical examples:
- When client devices are not capable of processing the required number of streams simultaneously.
- When it is required to synthesize multiple live videos into one single view. For example, to display the teacher's video and the students' videos in a synthesized view.
- When it is required to synthesize multiple audios into one single stream, especially for the voice chatroom scenarios.
Why stream mixing?
- It reduces the complexity of development. For example, when multiple users co-host an interactive live streaming event, it's much easier to receive and play just one single mixed stream rather than to receive and play multiple streams and do the screen layout for each stream individually.
- It reduces the requirements on the client device's performance and network bandwidth. Having more streams to process means more system resources and network bandwidth are required. With stream mixing, the burden of processing multiple streams is removed from the client side.
- It makes it much easier to forward multiple streams to multiple CDNs. You can achieve this by doing simple output stream configurations for stream mixing tasks.
- When it is required to record multiple streams for future playback, the recording can be done on the CDN to which the mixed stream is forwarded.
- Stream mixing also makes content moderation easier because it can be done by checking the mixed stream rather than checking multiple streams individually.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you complete the following:
- Create a project in ZEGOCLOUD Admin Console and get the AppID and AppSign of your project.
- Refer to the Quick Start doc to complete the SDK integration and basic function implementation.
- Contact us to activate the Stream Mixing service.
)
Manual stream mixing
With the manual stream mixing, you can customize the stream mixing tasks. which is often used for multiple users to co-host an interactive live streaming event and co-hosting across rooms.
To implement the stream mixing with SDK or ZEGO server API, refer to the Start stream mixing and Stop stream mixing.
The following describes how to implement the manual stream mixing in detail.
- Before starting a stream mixing task, the streams to be mixed must already exist in the room.
- A client can start a stream mixing task to mix those streams published by other clients in the same room while itself doesn't have to publish any streams first. If it does publish streams to the room, then these streams can also be included for mixing.
Set up a stream mixing task
ZegoMixerTask is a class defined in the SDK for configuring a stream mixing task. The configuration parameters include the layout of input streams, the outputs, and others.
1. Create a stream mixing task object
Create a stream mixing task object using the constructor ZegoMixerTask, and then call the instance methods to set up the input and output parameters.
ZegoMixerTask task = new ZegoMixerTask("task1");2. Optional: Set up the video configuration of the mixed stream
Set up the video configuration of the mixed stream
If the streams to be mixed are all audio-only, no video settings are required.
The default settings are:
- Resolution: 360P
- Frame rate: 15 fps
- Bitrate: 600 Kbps
// After the ZegoMixerVideoConfig object is created, set the values of the properties of videoConfig as needed. If not specified, the SDK uses the default settings (360p, 15fps, 600kbps).
ZegoMixerVideoConfig videoConfig = new ZegoMixerVideoConfig();
videoConfig.width = 360;
videoConfig.height = 640;
videoConfig.fps = 15;
videoConfig.bitrate = 600;
task.setVideoConfig(videoConfig);3. Optional: Set up the audio configuration of the mixed stream
Set up the audio configuration of the mixed stream
The default audio bitrate is 48 kbps.
// After the ZegoMixerVideoConfig object is created, set the values of the properties of audioConfig as needed. If not specified, the SDK uses the default settings (48kbps, mono audio channel, and the default audio codec).
ZegoMixerAudioConfig audioConfig = new ZegoMixerAudioConfig();
audioConfig.bitrate = 48;
audioConfig.channel = ZegoAudioChannel.MONO;
audioConfig.codecID = ZegoAudioCodecID.DEFAULT;
task.setAudioConfig(audioConfig);4. Set up the input streams
For each input stream, create a ZegoMixerInput object and set up the video layout settings by setting up the layout property of the ZegoMixerInput object.
- By default, a stream mixing task can have up to 9 input streams. If you need to have more input streams, contact ZEGOCLOUD Technical Support for assistance.
- For an audio-only input stream (defined in the
ContentTypeparameter of the input stream), there is no need to set thelayoutparameter.
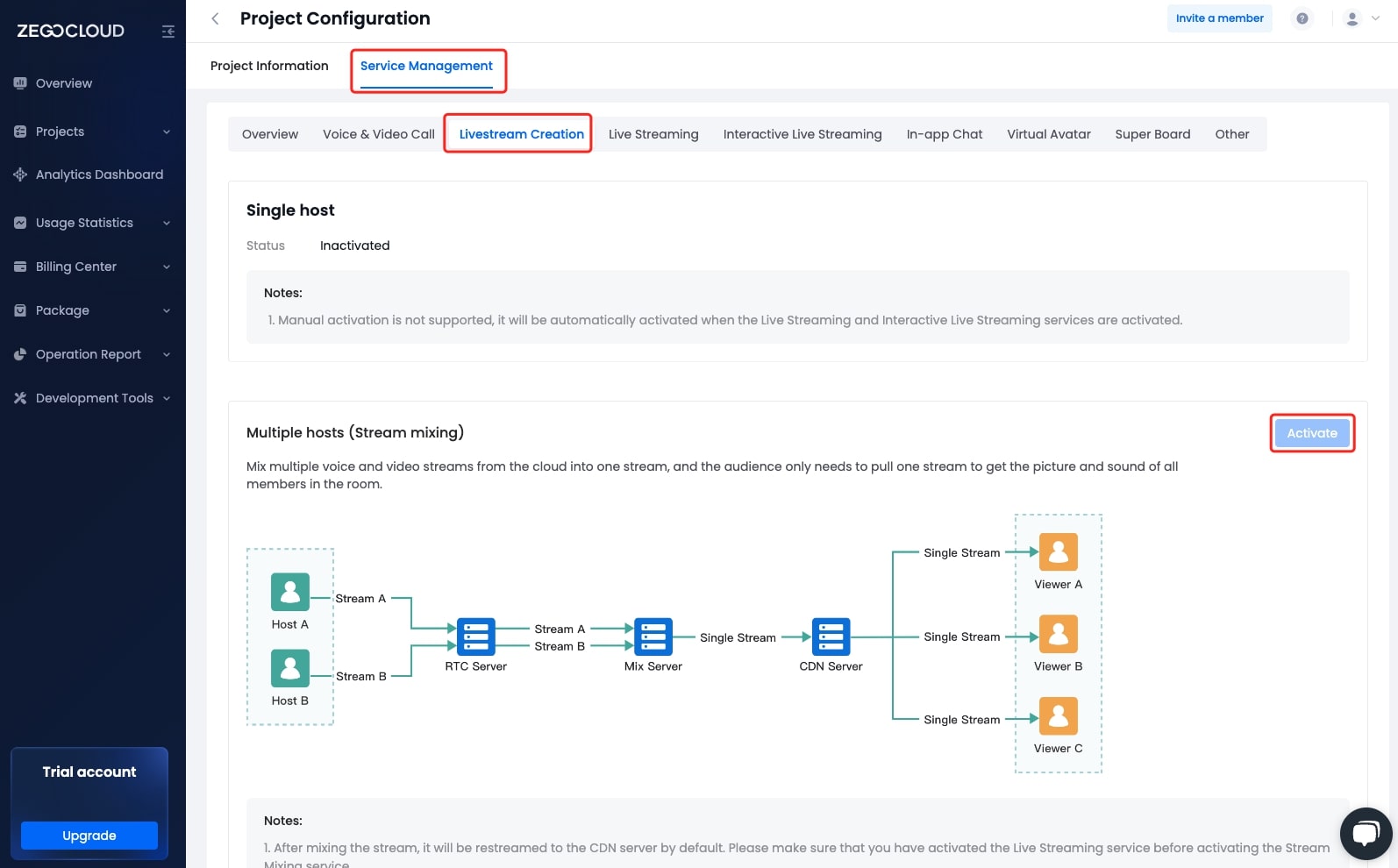
The layout of the input stream takes the upper left corner of the mixed output stream view as the origin of the coordinate system. Set the layout of the input stream according to the origin, that is, pass new Rect(left, top, right, bottom) into the layout parameter of the input stream.
In addition, the layer level of the input stream is determined by the position of the input stream in the input stream list. The further back the order in the list, the higher the layer level.
The following describes the Rect parameter:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
left |
Corresponds to the x coordinate of the upper left corner of the input stream view. |
top |
Corresponds to the y coordinate of the upper left corner of the input stream view. |
right |
Corresponds to the x coordinate of the lower righ corner of the input stream view. |
bottom |
Corresponds to the y coordinate of the lower righ corner of the input stream view. |
Let's suppose the following:
- You want to start a stream mixing task with the resolution of an output stream is 375 × 667.
- The coordinates of the upper-left corner of a stream are (50, 300), and the coordinates of its lower-right corner are (200, 450). Then, the
layoutparameter isnew Rect(50, 300, 200, 450).
Then, the position of this stream in the mixed stream can be illustrated as follows:
)
You can use the following example code to implement common output layouts: two views side by side, four views tiled vertically, one large view tiled with two small views suspended.
In the following examples, the resolution of the video screen layout is set as 360 × 640.
Layout 1: two views side by side
)
/** Create an input stream list. */
ArrayList<ZegoMixerInput> inputList = new ArrayList<>();
/** Configue the first input stream, including the streamID (the real ID of the input stream), input type, layout, etc.*/
ZegoMixerInput input_1 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_1", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(0, 0, 180, 640));
inputList.add(input_1);
/** Configue the second input stream. */
ZegoMixerInput input_2 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_2", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(180, 0, 360, 640));
inputList.add(input_2);
/** Set up the input steam list for the stream mixing task. */
task.setInputList(inputList);Layout 2: four views tiled vertically
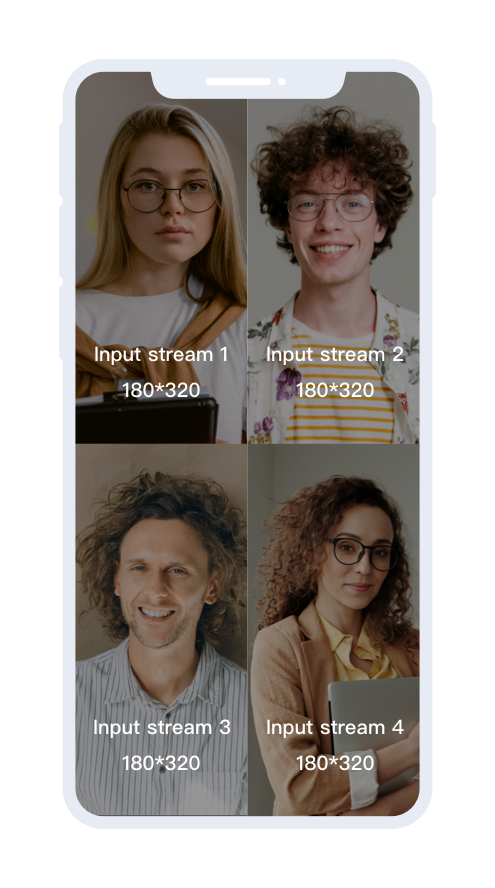)
/** Create an input stream list. */
ArrayList<ZegoMixerInput> inputList = new ArrayList<>();
/** Configue the first input stream, including the streamID (the real ID of the input stream), input type, layout, etc.*/
ZegoMixerInput input_1 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_1", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(0, 0, 180, 320));
inputList.add(input_1);
/** Configue the second input stream. */
ZegoMixerInput input_2 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_2", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(180, 0, 360, 320));
inputList.add(input_2);
/** Configue the third input stream. */
ZegoMixerInput input_3 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_3", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(0, 320, 180, 640));
inputList.add(input_3);
/** Configue the fourth input stream. */
ZegoMixerInput input_4 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_4", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(180, 320, 360, 640));
inputList.add(input_4);
/** Set up the input steam list for the stream mixing task. */
task.setInputList(inputList);Layout 3: one large view tiled with two small views suspended
)
The layer level of the input stream is determined by the position of the input stream in the input stream list. The further back the order in the list, the higher the layer level. As shown in the code below, the layer of input stream 2 and input stream 3 is higher than that of input stream 1, so streams 2 and 3 hover over the screen of input stream 1.
/** Create an input stream list. */
ArrayList<ZegoMixerInput> inputList = new ArrayList<>();
/** Configue the first input stream, including the streamID (the real ID of the input stream), input type, layout, etc.*/
ZegoMixerInput input_1 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_1", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(0, 0, 360, 640));
inputList.add(input_1);
/** Configue the second input stream. */
ZegoMixerInput input_2 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_2", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(230, 200, 340, 400));
inputList.add(input_2);
/** Configue the third input stream. */
ZegoMixerInput input_3 = new ZegoMixerInput("streamID_3", ZegoMixerInputContentType.VIDEO, new Rect(230, 420, 340, 620));
inputList.add(input_3);
/** Set up the input steam list for the stream mixing task. */
task.setInputList(inputList);5. Set up the mixing outputs
A stream mixing task can have up to 3 outputs.
In the following code example, the stream mixing task generates an output with stream name output_streamid_1, which will be published to the ZEGO server.
/** Create an output stream object. */
ZegoMixerOutput mixerOutput = new ZegoMixerOutput("output_streamid_1");
/** Construct the output stream list. */
ArrayList<ZegoMixerOutput> mixerOutputList = new ArrayList<>();
mixerOutputList.add(mixerOutput);
/** Set up the output stream list for the stream mixing task. */
task.setOutputList(mixerOutputList);6. Optional: Set up the watermark of the mixed stream
Set up the watermark of the mixed stream
If you need to add a watermark to the output stream, contact ZEGOCLOUD Technical Support to get the URL of the watermark image.
In the following code example, a ZEGO Logo watermark is placed at the upper-left corner of the output layout.
/** Create a watermark object. */
ZegoWatermark watermark = new ZegoWatermark();
// You need to send the watermarke image to ZEGOCLOUD technical support team, and then get the value of watermark.imageURL from the team.
watermark.imageURL = "preset-id://zegowp.png";
watermark.layout.top = 0;
watermark.layout.left = 0;
watermark.layout.right = 300;
watermark.layout.bottom = 200;
/** Set up the watermark for the stream mixing task. */
task.setWatermark(watermark);7. Optional: Set up the background image of the mixed stream
Set up the background image of the mixed stream
If you need to add a background image to the output stream, contact ZEGOCLOUD Technical Support to get the URL of the background image.
task.setBackgroundImageURL("preset-id://zegobg.png");8. Optional: Set up the event callback related sound level of the mixed stream
Set up sound level event callback
If you need to receive the event notification related to the sound level of the mixed stream, set the enableSoundLevel parameter to True to listening for the event callback.
The SDK sends out the sound level of each stream through the onMixerSoundLevelUpdate callback when you play the mixed stream.
9. Optional: Set up advanced configurations
Set up advanced configuration
You can use advanced configurations to achieve some special requirements, for example, to specify the video encoding format.
For more information about the advanced configurations, contact ZEGOCLOUD Technical Support.
There is no need to set up advanced configurations for common scenarios.
// Specify the video encoding format of the output stream a vp8, which requires a particular streaming protocol.
HashMap advancedConfig = new HashMap();
advancedConfig.put("video_encode", "vp8");
task.setAdvancedConfig(advancedConfig);
// If the video coding format of the output stream is set to vp8, then you need to set the audio codec to LOW3 to make it take effect.
ZegoMixerAudioConfig audioConfig = new ZegoMixerAudioConfig();
audioConfig.codecID = ZegoAudioCodecID.LOW3;
task.setAudioConfig(audioConfig);Start the stream mixing task
After configuring the ZegoMixerTask object, call the corresponding method to start the stream mixing task. If the stream mixing task doesn't start successfully, handle the failure in the callback that returns the execution result.
- Function prototype:
/**
* Start the stream mixing task.
*
* In consideration of the performance of client devices, stream mixing is performed on ZEGO's cloud servers.
* When you call this method, ZegoExpressEngine sends a stream-mixing request to ZEGO's backend service running on the cloud, which will then start mixing the streams configured in the task and the one being published by the current user (if any).
* If any exception occurs in starting up the task, for example, the specified stream does not exist, the related error code will be provided in the callback. Refer to the document [https://doc-en.zego.im/article/5548.html] for details of the error codes.
* If a certain input stream gets lost when the stream mixing is still in progress, the stream mixing task will automatically retry to pull that stream with a timeout of 90 seconds, after which no more retries will be attempted.
* @param task: The stream mixing task object.
* @param callback: The callback to report the result of task startup.
*/
public void startMixerTask(ZegoMixerTask task, IZegoMixerStartCallback callback)- Sample code:
engine.startMixerTask(task, new IZegoMixerStartCallback() {
@Override
public void onMixerStartResult(int errorCode, JSONObject extendedData) {
if (errorCode != 0) {
//Failed to start or update the stream mixing task. Task update failure will affect the current task that is in progress.
}
else {
//The stream mixing task is started or updated successfully.
}
}
});Update the configurations of the stream mixing task
When you need to change the stream mixing task, for example, when the number of input streams increases or decrease, or the bitrate of the output stream needs to be adjusted, you can update the stream mixing task object with the new configurations and then call the startMixerTask method again.
When updating the configuration of a stream mixing task, you must not change the taskID.
Stop the stream mixing task
To stop a stream mixing task, call the stopMixerTask method, with the corresponding task ID passed to the taskID parameter.
- Function prototype:
/**
* Stop the stream mixing task.
*
* Similar to [startMixerTask], when you call this method, ZegoExpressEngine sends a request to ZEGO's backend service running on the cloud to stop the specified stream mixing task.
* If the developer starts the next stream mixing task without stopping the previous stream mixing task, the previous stream mixing task will not stop automatically, but it will stop 90 seconds after all its input streams no longer exist.
* It's worth reminding that developers should stop the previous stream mixing task before starting the next one, to prevent that the viewers are still pulling the output stream of the previous stream mixing task event after the host already started a new task.
* @param task: The stream mixing task object.
* @param callback: The callback to report the result of ending the task.
*/
public void stopMixerTask(ZegoMixerTask task, IZegoMixerStopCallback callback);- Sample code:
/** Pass in the taskID of the steam mixing task to be stopped. */
engine.stopMixerTask("task1");Automatic stream mixing
- Before starting a stream mixing task, the streams to be mixed must already exist in the room.
- A client can start a stream mixing task to mix those streams published by other clients (audio streams only) in the same room while itself doesn't have to publish any streams first. If it does publish streams to the room, then these streams can also be included for mixing.
Set up a stream mixing task
ZegoAutoMixerTask is a class defined in the SDK for configuring a stream mixing task. The configuration parameters include the layout of input streams, the outputs, and others.
// Stream mixing task object.
public class ZegoAutoMixerTask {
public String taskID = "";// Task ID of the stream mixing task
public String roomID = "";// Room ID of the stream mixing task
public ZegoMixerAudioConfig audioConfig = new ZegoMixerAudioConfig();// Set up the audio configuration of the mixed stream.
public ArrayList<ZegoMixerOutput> outputList = new ArrayList();// Set up the list of mixing outputs.
public boolean enableSoundLevel = false;// Set up the event callback related sound level of the mixed stream.
public ZegoAutoMixerTask() {
}
}1. Create an auto stream mixing task object
Create an auto stream mixing task object and then call the instance methods to set up the input and output parameters.
- The task ID must be unique within a room. We recommend you set the room ID as the task ID.
- The room ID must have already existed; otherwise, the stream mixing will fail.
ZegoAutoMixerTask task = new ZegoAutoMixerTask();
task.taskID = "taskID1";
task.roomID = "roomID1";2. Optional: Set up the audio configuration of the auto mixed stream
Set up the audio configuration of the auto mixed stream
To set up the audio configuration of the auto mixed audio streams, call the ZegoMixerAudioConfig method, including the audio bitrate, channels, codec ID, and audio mix mode.
ZegoMixerAudioConfig audioConfig = new ZegoMixerAudioConfig();
audioConfig.bitrate = 48;/** Audio bitrate, unit: kbps, use 48 kbps by default. This can't be changed after stream mixing starts. */
audioConfig.channel = MONO;/** Audio channel, use Mono by default */
audioConfig.codecID = DEFAULT;/** Codec ID, use DEFAULT by default. */
audioConfig.mixMode = RAW;/** Audio mix mode, use RAW by default. */
task.audioConfig = audioConfig;To modify the audio channel, set the channel property accordingly. The following are the supported channels:
| Enumerated value | Description | Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| UNKOWN | Unkown | - |
| MONO | Mono | Mono-only scenario. |
| STEREO | Stereo | Stereo scenario. |
To modify the codec ID, set the codecID property accordingly. The following are the supported codec IDs:
| Enumerated value | Description |
|---|---|
| DEFAULT | default |
| NORMAL | Normal |
| NORMAL2 | Normal2 |
| NORMAL3 | Normal3 |
| low | Low |
| low2 | Low2 |
| low3 | Low3 |
To modify the mix mode, set the mixMode property accordingly. The following are the supported audio mix modes:
| Enumerated value | Description | Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| RAW | Default mode. | Scenarios with no special need for audio. |
| FOCUSED | Focus mode. Highlights the sound of a stream in a multi-channel audio stream. | The scenario where the sound of a stream needs to be highlighted. |
3. Set up the auto mixing outputs
To set up the auto mixing outputs, call the ZegoMixerOutput method to set the output list.
And you can play the mixed stream according to the output-stream of the outputs.
ArrayList<ZegoMixerOutput> outputList = new ArrayList<>();
ZegoMixerOutput output = new ZegoMixerOutput("output-stream");/** Mixing output target, URL or streamID. */
outputList.add(output);
task.outputList = outputList;4. Optional: Set up the event callback related sound level of the auto mixed stream
Set up sound level event callback
If you need to receive the event notification related to the sound level of the auto mixed stream, set the enableSoundLevel parameter to True to listening for the event callback.
The SDK sends out the sound level of each stream through the onAutoMixerSoundLevelUpdate callback when you play the mixed stream.
Start the auto stream mixing task
After configuring the ZegoAutoMixerTask object, call the startAutoMixerTask method to start the stream mixing task.
And the SDK sends out the result notifications through the onAutoMixerSoundLevelUpdate callback.
MixerMainActivity.engine.startAutoMixerTask(task, new IZegoMixerStartCallback() {
@Override
public void onMixerStartResult(int errorCode, JSONObject var2) {
if (errorCode != 0) {
// Auto stream mixing task started successfully.
}
}
});Stop the auto stream mixing task
To stop a stream mixing task, call the stopAutoMixerTask method.
- To start a new auto stream mixing task in the same room, call the
stopAutoMixerTaskmethod to stop the auto stream mixing task first. (In order to avoid the situation that when a host has started the next auto stream mixing stream task and mixed his/her stream with other hosts, while the audience is still playing the output stream of the old auto stream mixing task.) - If the user does not actively stop the current auto stream mixing task, the task will automatically stop after the room does not exist or the input stream does not exist for 90 seconds.
// Pass in the task object of the steam mixing task to be stopped.
[[ZegoExpressEngine sharedEngine] stopAutoMixerTask:self.autoMixerTask callback:^(int errorCode) {
if(errorCode == 0) {
///Auto stream mixing task stopped successfully.
}
}];Full-automatic stream mixing
To fully-automatical mix the audio streams in each room, contact the ZEGOCLOUD Technical Support.
FAQ
Can I forward the mixed stream to a third-party CDN or even multiple CDNs?
Yes. To forward the mixed stream to a third-party CDN, specify the CDN URL in the
targetproperty of theZegoMixerOutputobject. The URL must be in RTMP format:rtmp://xxxxxxxx.To forward the mixed stream to multiple CDNs, create multiple
ZegoMixerOutputobjects accordingly, and put them into theoutputListof theZegoMixerTaskobject.
When the aspect ratio of the
ZegoMixerInput'slayoutparameter doesn't match the resolution of the input stream itself, how does the SDK handle the video cropping?The SDK scales the video proportionally.
Let's suppose the following:
The resolution of an input stream is
720 × 1280, whose aspect ratio is9:16.The
layoutparameter of theZegoMixerInputobject is[left:0 top:0 right:100 bottom:100], whose aspect ratio is1:1.Then, the SDK displays the middle part of the video and cuts off the upper part and lower part.
If all the hosts of the same live broadcast want their audience to see that their own video is located in the larger window in the mixed stream layout. How to configure the stream mixing task?
The hosts can start a stream mixing task with their own output stream layout.
Let's suppose the following:
Host A and Host B are co-hosting a live streaming session.
Host A is publishing Stream A.
Host B is publishing Stream B.
Then, Host A and Host B can respectively start a stream mixing task with different video layouts:
In Host A's stream mixing task, the video size (width and height) of stream A is larger than that of stream B.
In Host B's stream mixing task, the video size (width and height) of stream B is larger than that of stream A.
For a live streaming session with two hosts, what are the pros and cons of the following two options for starting the stream mixing?
A. To start the stream mixing immediately after the first host starts publishing a stream.
B. To start the stream mixing only after both hosts start publishing streams.
Option Pros Cons Option A It's easy to implement. The viewers can play the mixed stream right at the beginning and don't need to do any stream switching in the middle. It costs more CDN usage because the stream mixing starts earlier. Option B It costs less CDN usage because the stream mixing starts later. The implementation is more complicated compared to option A. The viewers need to play the first host's stream at the beginning and then switch to the mixed stream later. Does the SDK support round or square video layout for stream mixing?
The SDK doesn't support round video layout for stream mixing.
You can set up square video layouts by configuring the
layoutparameter of the input streams.