- Documentation
- Live Streaming
- Develop your app
- Live Streaming
- Implement a basic live streaming
Implement a basic live streaming
Introduction
This guide describes how to implement basic audio and video functions with the ZEGO Express SDK.
Basic concepts:
ZEGO Express SDK: The real-time audio and video SDK developed by ZEGO to help you quickly build high-quality, low-latency, and smooth real-time audio and video communications into your apps across different platforms, with support for massive concurrency.
Stream publishing: The process of the client app capturing and transmitting audio and video streams to the ZEGO Real-Time Audio and Video Cloud.
Stream playing: The process of the client app receiving and playing audio and video streams from the ZEGO Real-Time Audio and Video Cloud.
Room: The service for organizing groups of users, allowing users in the same room to send and receive real-time audio, video, and messages to each other.
- Logging in to a room is required to perform stream publishing and playing.
- Users can only receive notifications about changes in the room they are in (such as new users joining the room, existing users leaving the room, new audio and video streams being published, etc.).
For more basic concepts, refer to the Glossary.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you complete the following steps:
- Create a project in ZEGOCLOUD Admin Console, and get the AppID of your project.
- Integrate the ZEGO Express SDK into your project. For more details, see Integration.
Implementation steps
The following diagram shows the basic process of User A playing a stream published by User B:
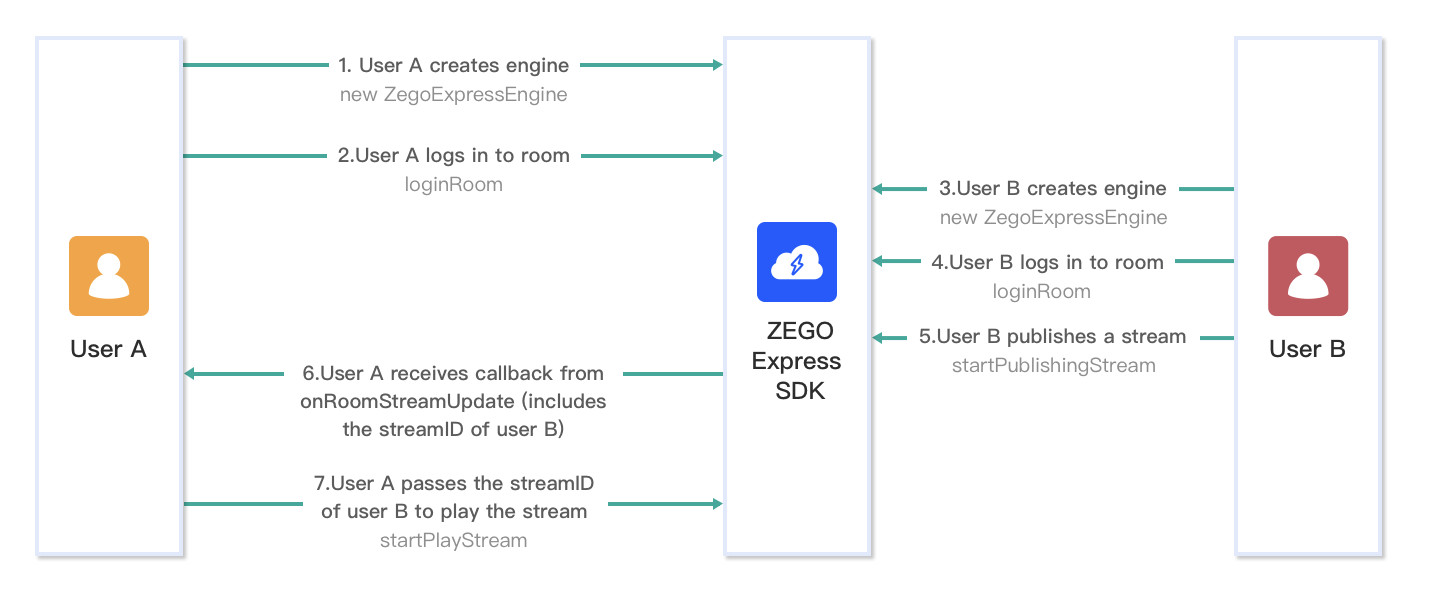)
The following sections explain each step of this process in more detail.
Create a ZegoExpressEngine instance
To create a singleton instance of the ZegoExpressEngine class, pass in your AppID as the appID parameter and the Server URL as the server parameter. You can obtain them from the ZEGOCLOUD Admin Console.
// Initialize the ZegoExpressEngine instance
const zg = new ZegoExpressEngine(appID, server);Optional: Listen for and handle the event callbacks
After you create a ZegoExpressEngine instance, you can call the on method to listen for and handle various event callbacks as needed.
The following sample code demonstrates how to listen for and handle the roomStateUpdate callback. For more event callbacks, see ZegoRTCEvent and ZegoRTMEvent.
zg.on('roomStateUpdate', (roomID, state, errorCode, extendedData) => {
if (state == 'DISCONNECTED') {
// Disconnected from the room.
// ...
}
if (state == 'CONNECTING') {
// Connecting to the room.
// ...
}
if (state == 'CONNECTED') {
// Connected to the room.
// ...
}
})Check your browser's WebRTC support
Before starting to publish or play a stream, you can call the checkSystemRequirements method to check if your browser supports WebRTC.
For more information about the browser versions supported by the SDK, see Browser compatibility.
const result = await zg.checkSystemRequirements();
// The [result] indicates whether it is compatible. It indicates WebRTC is supported when the [webRTC] is [true]. For more results, see the API documents.
console.log(result);
// {
// webRTC: true,
// customCapture: true,
// camera: true,
// microphone: true,
// videoCodec: { H264: true, H265: false, VP8: true, VP9: true },
// screenSharing: true,
// errInfo: {}
// }For more about the parameters of the returned results, refer to the parameter description of this ZegoCapabilityDetection method.
Log in to a room
When logging in to a room, you need to pass in a token for user authentication. To obtain the login token, see User privilege control.
To log in to a room, call the loginRoom with the following parameters:
- A unique room ID as the
roomIDparameter - The login token you obtained in the previous step
as the
tokenparameter - The user ID and user name as the
roomIDanduserNameparameter - Optional: Pass the corresponding object to the
configparameter based on the actual situation.
If the roomID does not exist, a new room will be created and you will log in automatically when you call the loginRoom method.
// Log in to a room. It returns `true` if the login is successful.
// The roomUserUpdate callback is disabled by default. To receive this callback, you must set the `userUpdate` property to `true` when logging in to a room.
const result = await zg.loginRoom(roomID, token, {userID, userName}, {userUpdate: true});Then, to listen for and handle various events that may happen after logging in to a room, you can implement the corresponding event callback methods of the event handler as needed. The following are some common event callbacks related to room users and streams:
roomStateUpdate: Callback for updates on current user's room connection status. When the current user's room connection status changes (for example, when the current user is disconnected from the room or login authentication fails), the SDK sends out the event notification through this callback.roomUserUpdate: Callback for updates on the status of other users in the room. When other users join or leave the room, the SDK sends out the event notification through this callback.roomStreamUpdate: Callback for updates on the status of the streams in the room. When new streams are published to the room or existing streams in the room stop, the SDK sends out the event notification through this callback.
- To receive the
roomUserUpdatecallback, you must set theisUserStatusNotifyproperty of the room configuration parameterZegoRoomConfigtotruewhen you call theloginRoommethod to log in to a room.
- To play streams published by other users in the room: you can listen for the
roomUserUpdatecallback, and when there is a stream added, call thestartPlayingStreammethod to start receiving and playing the newly added stream.
// Callback for updates on the current user's room connection status.
zg.on('roomStateUpdate', (roomID,state,errorCode,extendedData) => {
if (state == 'DISCONNECTED') {
// Disconnected from the room
}
if (state == 'CONNECTING') {
// Connecting to the room
}
if (state == 'CONNECTED') {
// Connected to the room
}
})
// Callback for updates on the status of ther users in the room.
zg.on('roomUserUpdate', (roomID, updateType, userList) => {
console.warn(
`roomUserUpdate: room ${roomID}, user ${updateType === 'ADD' ? 'added' : 'left'} `,
JSON.stringify(userList),
);
});
// Callback for updates on the status of the streams in the room.
zg.on('roomStreamUpdate', async (roomID, updateType, streamList, extendedData) => {
if (updateType == 'ADD') {
// New stream added, start playing the stream.
} else if (updateType == 'DELETE') {
// Stream deleted, stop playing the stream.
}
});Publish streams
To create a local audio and video stream, call the createZegoStream method. By default, the engine captures video data from the camera and captures audio data from the microphone.
After calling the createZegoStream method, you need to wait for the ZEGO server to return the media stream object (localStream) before any further operation.
// After calling the createZegoStream method, you need to wait for the ZEGO server to return the local stream object before any further operation.
const localStream = await this.zg.createZegoStream();
// Play preview of the stream
localStream.playVideo(document.querySelector("#local-video"));Optional: Set up the audio/video capturing parameters
If you don't want to use the SDK's default audio/video capturing settings, you configure the following parameters of the createZegoStream method with your own specific settings. For more details, see Custom video capture.
Optional: Render audio and video under different frameworks
The rendering of audio and video varies across different development frameworks. For more details, see Audio and Video Rendering under Different Frameworks (Web).
Then, to start publishing a local audio and video stream to remote users, call the startPublishingStream method with the following parameters:
- A stream ID as the
streamIDparameter - The media stream object obtained in the previous step as
localStreamparameter
- You need to implement your own business logic to set the values of
streamIDand make sure thestreamIDis globally unique within the scope of the AppID. - To publish multiple streams, call the
startPublishingStreammethod multiple times, making sure that each stream has a uniquestreamID.
// localStream is the MediaStream object created by calling creatStream in the previous step.
zg.startPublishingStream(streamID, localStream)Then, to listen for and handle various events that may happen after stream publishing starts, you can implement the corresponding event callback methods of the event handler as needed. The following are some common event callbacks related to stream publishing:
publisherStateUpdate: Callback for updates on stream publishing status. After stream publishing starts, if the status changes, (for example, when the stream publishing is interrupted due to network issues and the SDK retries to start publishing the stream again), the SDK sends out the event notification through this callback.
publishQualityUpdate: Callback for reporting stream publishing quality. After stream publishing starts, the SDK sends out the streaming quality data (resolution, frame rate, bit rate, etc.) regularly through this callback.
zg.on('publisherStateUpdate', result => {
// Callback for updates on stream publishing status.
// ...
})
zg.on('publishQualityUpdate', (streamID, stats) => {
// Callback for reporting stream publishing quality.
// ...
})Play streams
To start playing a remote audio and video stream from the ZEGO server, call the startPlayingStream method with the corresponding stream ID passed to the streamID parameter.
You can obtain the stream ID of the streams published by remote users from the callback roomStreamUpdate.
const remoteStream = await zg.startPlayingStream(streamID);
// The remote-video is the <div> element's id on your webpage.
remoteView.play("remote-video", {enableAutoplayDialog:true});Optional: Render audio and video under different frameworks
The rendering of audio and video varies across different development frameworks. For more details, see Audio and Video Rendering under Different Frameworks (Web) .
- Each
streamIDmust be globally unique within the AppID. - The
remoteVideoobject is the audio or video element on your webpage, which will be used to play out the audio or video. We recommend you enable theautoplayproperty of theremoteVideoobject. - Some browsers require you to mute the video if you enable the
autoplayproperty. In this case, we recommend you guide the users to manually unmute the video. - On iOS, users will need to manually play the video because iOS's restricted auto-play policy for video (changing this policy requires special processing at the business layer) makes it unable to automatically play video in web browsers on iOS.
Then, to listen for and handle various events that may happen after stream playing starts, you can implement the corresponding event callback methods of the event handler as needed. The following are some common event callbacks related to stream playing:
playerStateUpdate: Callback for updates on stream playing status. After stream playing starts, if the status changes (for example, when the stream playing is interrupted due to network issues and the SDK retries to start playing the stream again), the SDK sends out the event notification through this callback.
playQualityUpdate: Callback for reporting stream playing quality. After stream playing starts, the SDK sends out the streaming quality data (resolution, frame rate, bit rate, etc.) regularly through this callback.
zg.on('playerStateUpdate', result => {
// Callback for updates on stream playing status.
// ...
})
zg.on('playQualityUpdate', (streamID,stats) => {
// Callback for reporting stream playing quality.
})Test out the live streaming
We recommend you run your project on a real device. If your app runs successfully, you should hear the sound and see the video captured locally from your device.
To test out the real-time audio and video features, visit the ZEGO Express Web Demo, and enter the same AppID, Server and RoomID to join the same room. If it runs successfully, you should be able to view the video from both the local side and the remote side, and hear the sound from both sides as well.
In audio-only scenarios, no video will be captured and displayed.
Stop publishing and playing streams
To stop publishing a local audio and video stream to remote users, call the stopPublishingStream method with the corresponding stream ID passed to the streamID parameter.
zg.stopPublishingStream(streamID)Then, to destroy a local media stream, call the destroyStream method. After destroying the local media stream, you need to manually destroy the video element.
// localStream is the MediaStream object created when calling the createZegoStream method.
zg.destroyStream(localStream)Then, to stop playing a remote audio and video stream, call the stopPlayingStream method with the corresponding stream ID passed to the streamID parameter.
zg.stopPlayingStream(streamID)Log out of a room
To log out of a room, call the logoutRoom method with the corresponding room ID passed to the roomID parameter.
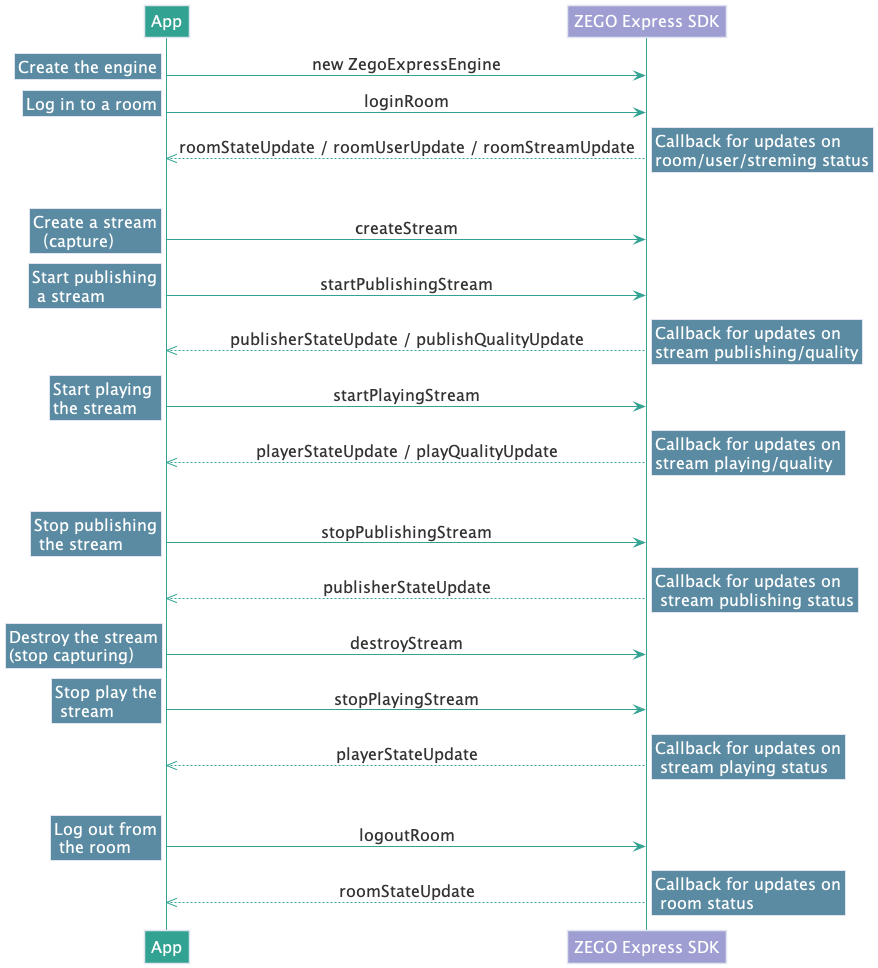
zg.logoutRoom(roomID)API call sequence diagram
The following diagram shows the API call sequence of the stream publishing and playing process:
)